DRAINAGE
Patient Education Material
Image-guided percutaneous drainage involves using a catheter (a thin tube) to drain an abscess or a collection of fluid or air under image guidance. The interventional radiologist will insert a flexible catheter through a small cut in your skin and will guide the catheter to the collection of fluid or air. The fluid or air will then be collected in a drainage bag.
Drainage catheters are available in a variety of sizes, shapes and types. The interventional radiologist will choose the catheter according to the type of fluid, along with other indications. If you are on any medication that prevents blood clotting, you will stop taking it before the procedure, if possible.
Percutaneous drainage can be performed as an in-patient or out-patient procedure. The puncture site and your vital signs will be monitored for 4-6 hours. You will experience some mild discomfort around the puncture site in the first few hours after the procedure. The interventional radiologist will periodically follow up using imaging to confirm that the abscess or fluid collection has gone.
US, FLUOROSCOPIC OR CT GUIDED DRAINAGE OF COLLECTIONS, ABCESS OR FLUID
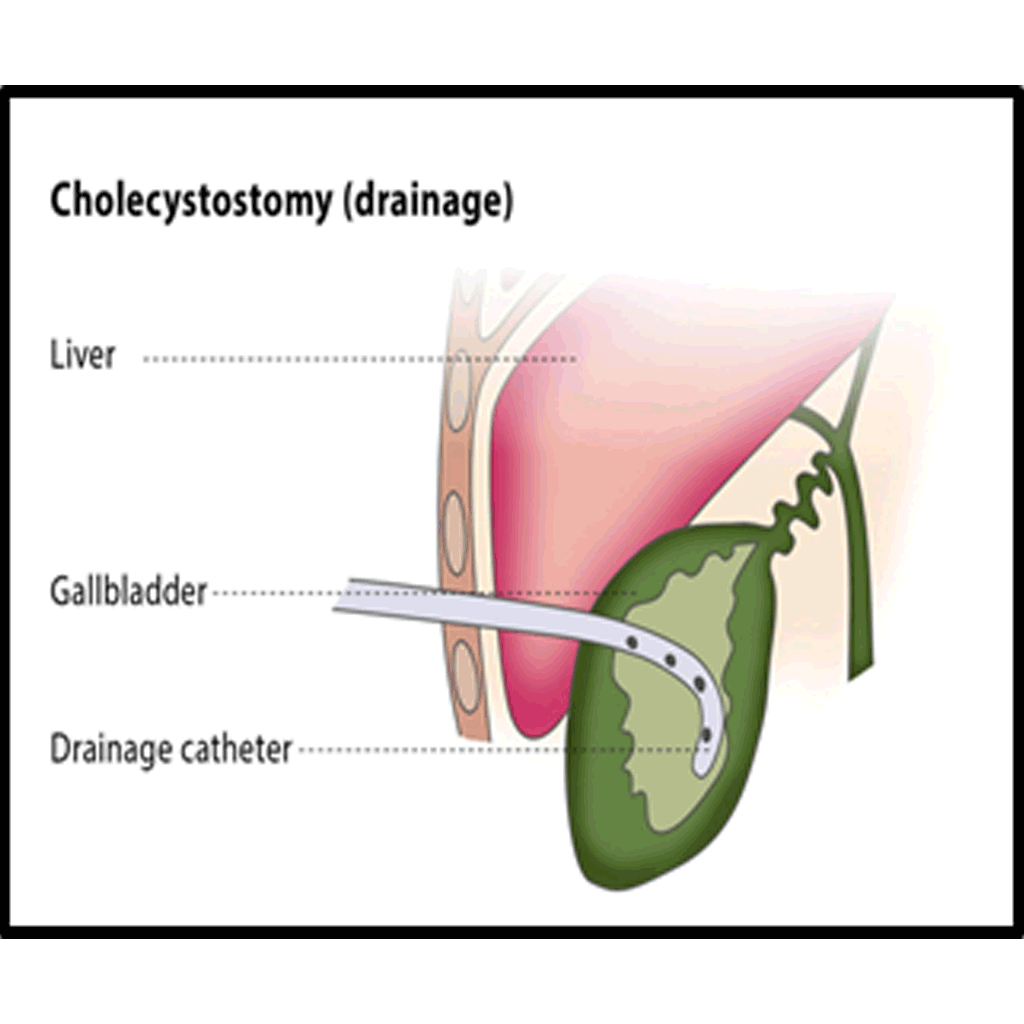
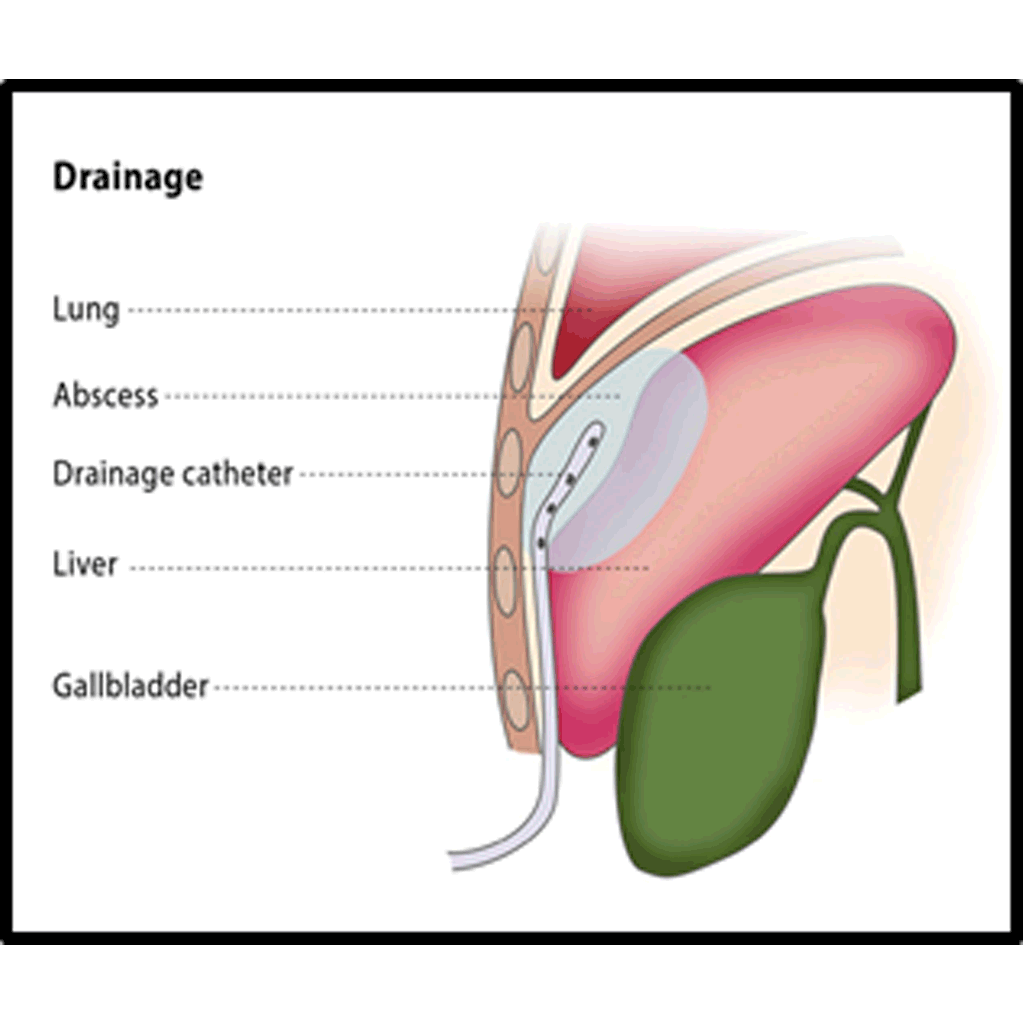
Percutaneous drainage is recommended to treat fluid or air collections that produce symptoms (such as pneumothorax, which is the collection of air or gas in the gap between the chest wall and the lungs). It can also treat recurrent fluid collections by using medication and is a minimally invasive method of draining abscesses. The percutaneous drainage procedure cures infected fluid/air collections in over 80% of patients, though failure occurs in 5-10% of patients
Kindly contact:
- One PKLI Avenue, DHA, Phase-6, Lahore, Pakistan.
- info@pkli.org.pk
- +92 42 111 117 554

